Everyone uses electronic devices that have an autonomous power source. In most cases, these are disposable batteries called batteries.
Content
What is a battery?
A battery is an autonomous galvanic battery for various devices powered by electric energy. The principle of operation of batteries is based on the use of an irreversible chemical reaction of two metals (or their oxides) in an electrolyte, accompanied by the appearance of an electromotive force. Due to the irreversibility of the reactions associated with the formation of electricity in such power sources, they are called primary.
Secondary power sources (batteries) operate using the same principles of operation, but with chemicals that can recover after a charge, making them reusable.
Battery markings
According to the IEC standard (International Electrotechnical Commission), galvanic current sources are marked based on the composition of the electrolyte and active metal used in their design.
According to this classification, there are 5 of the most common types of round (cylindrical) batteries: salt, alkaline, lithium, silver and air-zinc. The letter R in their designation means a round shape (from English round).
Salt batteries (R). They have a cathode of zinc, an anode of manganese dioxide and an electrolyte of ammonium and zinc chlorides. They provide a voltage of 1.5 volts, have a small capacity, high self-discharge and low shelf life (up to 2 years). At low temperatures, they are inoperative.
Salt batteries the cheapest and have mediocre technical specifications. In everyday life, they are also called zinc-carbon and carbon-zinc.

Alkaline batteries (LR). They have a cathode of zinc, an anode of manganese dioxide and an electrolyte of alkali metal hydroxide. They have a voltage of 1.5 volts, increased capacity, low self-discharge and a long shelf life of up to 10 years. They remain operational at low temperatures up to -20 degrees.
These current sources are inexpensive, in everyday life they are also called alkaline and alkaline manganese.
Lithium Batteries (CR). They have a lithium cathode, a manganese dioxide anode and an organic electrolyte. They have a voltage of 3 volts, a large capacity, a small self-discharge and a long shelf life of up to 10-12 years. They remain operational at low temperatures up to -40 degrees. These current sources are quite expensive.
Silver batteries (SR). They have a cathode of zinc, an anode of silver oxide and an electrolyte of alkali metal hydroxide. They have a voltage of 1.55 volts, high capacity, small self-discharge and a long shelf life of up to 10 years. They remain operational at low temperatures up to -30 degrees. Typically used in watches. In everyday life they are also called silver-zinc.
Zinc Air Elements (PR). They have a zinc cathode, an oxygen anode, and an alkali metal hydroxide electrolyte.
These current sources are the cleanest from an environmental point of view, which is why they are widely used in special medical devices, but have the shortest life (several weeks after opening the package). They have an average cost, have a voltage of 1.2-1.4 volts and a very high capacity (2-3 times more than lithium-ion cells), they remain operational at temperatures from -20 to +35 degrees.
During storage, such elements must be sealed to prevent self-discharge. Subject to the correct storage conditions (ensuring tightness), they have low self-discharge and can be stored for several years.
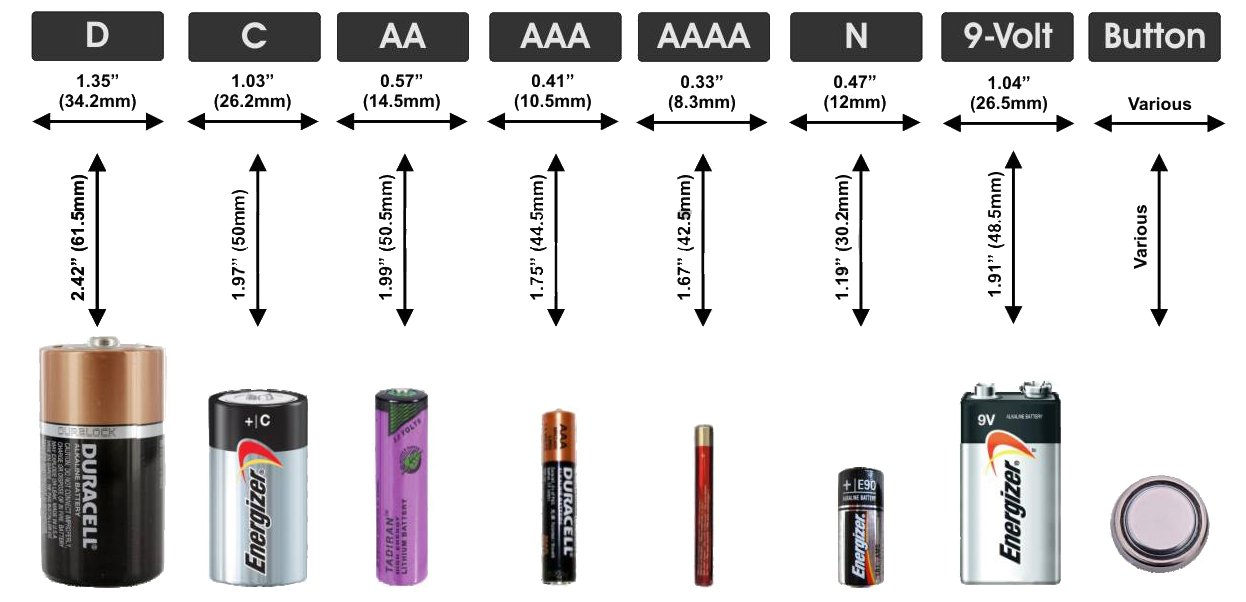
Types of batteries in size and their designations
At present, the battery designation system adopted in the USA is very widespread in the world. It is based on the physical dimensions of power supplies. The following are the most common ones.
| Title | Marking and Type | Diameter mm | Height mm | Capacity, mAh * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Saline (R23) Alkaline (LR23) | 17 | 50 | n / a |
| AA | Saline (R6) Alkaline (LR6) Lithium (FR6) | 14,5 | 50,5 | 1100-3500 |
| AAA | Saline (R03) Alkaline (LR03) Lithium (FR03) | 10,5 | 44,5 | 540-1300 |
| AAAA | Alkaline (LR8D425) | 8,3 | 42,5 | 625 |
| B | Alkaline (LR12) | 21,5 | 60 | 8350 |
| C | Saline (R14) Alkaline (LR14) | 26,2 | 50 | 3800-8000 |
| D | Saline (R20) Alkaline (LR20) | 34,2 | 61,5 | 8000-19500 |
| F | Saline (R20) Alkaline (LR20) | 33 | 91 | n / a |
| N | Saline (R1) Alkaline (LR1) | 12 | 30,2 | 1000 |
| 1 / 2AA | Saline (R14250) | 14,5 | 25 | 250 |
| R10 | Saline (R10) | 21,5 | 37,3 | 1800 |
* Technologies are developing very fast because of this, not today the capacity may be higher than indicated in the table (2018)
Next, the sizes of the batteries and their characteristics will be discussed in more detail.
Battery pills
These are circular circular current sources, they are also called coins or buttons. There are many varieties of batteries of this type, the main of which are:
- CR lithium cells with sizes from 927 to 3032 (where the first one or two digits is the diameter in millimeters, and the last two digits are the thickness, in tenths, of a millimeter) by 3 volts.
- Alkaline special disk elements LR (sizes 43, 44, 54) for one and a half volts for watches and miniature devices.
- SR disk batteries in sizes from 41 to 932 with silver oxide for watches at 1.55 volts.
- Air-zinc PR elements of sizes 5, 10, 13, 312, 630 and 675 at 1.2 volts.
Types of Popular Batteries
Due to its high capacity and convenience, cylindrical batteries gained great popularity. Consider the most popular ones available.
AA. This is one of the most common types of 1.5 volt cylindrical batteries with a size of 14.5 x 50.5 mm. They are designated by the IEC standard as Lr6 (alkaline), R6 (carbon-zinc), FR6 (lithium). In everyday life are called finger.
AAA. These are very common 1.5 volt current sources measuring 10.5 x 44.5 mm. Are marked LR03 for alkaline cells and similarly to AA cells for other types of batteries (R03, FR03 and so on). Colloquially called pinky batteries.
Type C. Elements R14 and Lr14 1.5 volts are salt and alkaline. In common parlance, they are called average. They have a size of 26.2x50 mm and are approximately equal in length to AA batteries, which is why they are sometimes replaced by using special overlays.
Type D. Are designated Lr20 (alkaline), R20 (saline). They have a size of 34.2x61.5 mm and a large capacity of 8000-12000 mAh. Popularly, these batteries are called "large" or "barrels." These are the very first 1.5 volt batteries that began to be produced back in 1898 for flashlights.
PP3. According to IEC classification, 6LR61 (alkaline), 6F22 (saline) and 6KR61 (lithium) are designated. In everyday life, these batteries are called "Crown". They have dimensions of 48.5x26.5x17.5 mm, voltage 9v, capacity from 400 (salt) to 1200 mAh (lithium).
Structurally, they are a combination of six (salt or alkaline) or three (lithium) elements in one housing.
Exotic Battery Types
A. These are salt batteries with a cylindrical shape and a half volts, designated R23 according to IEC standard. They have a size of 17x50 mm and were popular in older laptop models and non-standard devices. Currently practically not applied.
AAAA. These are alkaline cylindrical mini batteries LR61 one and a half volts in size 8.3 by 42.5 mm. They are used in thin flashlights (in the form of a pen), glucometers, laser pointers and powerful styluses.
Type B. Salt R12 and alkaline LR12 cylindrical elements of this type are available in size 21.5x60 mm at 1.5 v. Usually used in flashlights.
Type F. These 1.5 volt power supplies are designated L25 and LR25. They have a capacity of 10.5 (saline) to 26 (alkaline) Ah / h. They have a size of 33x91 mm.
Type N. Batteries R1 and Lr1 have a capacity of 400-1000 mAh, voltage - 1.5 volts, size 12x30.2 mm.
1 / 2AA. CR14250 is designated for 3 volt lithium manganese (Li ‑ MnO2) and ER14250 for 3.6 volt lithium-thionyl chloride (Li ‑ SOCl2) batteries. They measure 14x25 mm.
R10. These are 1.5 volt batteries, which were produced in the USSR under the marking 332. They have a size of 21x37 mm. They are currently available in very limited quantities.
There are 2R10 batteries with dimensions of 21.8 x 74.6 mm at 3 volts, called Duplex because they inside contain two 1.5 volts R10 cells connected in series.
A23. This is an alkaline battery (according to the classification of IEC - 8LR932) for 12 v with a size of 10.3x28.5 mm. Usually consists of 8 LR932 elements connected in series. Suitable for radio controlled products.
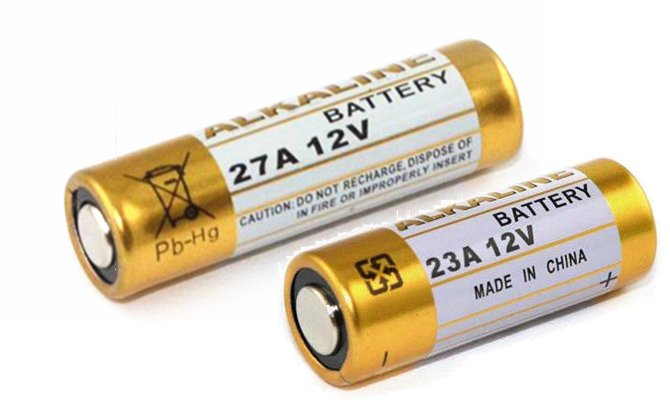

A27. This is an alkaline battery (according to IEC classification - 8LR732) for 12 v, size 8x28.2 mm. Usually consists of 8 LR632 elements connected in series. It is used for products controlled by radio, electric lighters and electronic cigarettes.
Widespread in various devices are also flat batteries of 4.5 and 9 volts.
3336. According to IEC standards, 3LR12 (alkaline), 3R12 (saline) are designated in common use as “square”. They have been produced since 1901 for flashlights. They have a voltage of 4.5 volts, capacity from 1200 to 6100 mAh, size 67x62x22 mm. Structurally, they are 3 series-connected elements of R12, combined in one housing.
The large abundance of power supplies available on the market makes it easy to find the right battery for each particular case. At the same time, it is better to focus on well-known brands that produce good quality products worth the money spent.
If you find that some kind of battery is missing, please write its marking in the comments and we will definitely add it.









A battery refers to two or more batteries combined into a single current source. “Krona” is really a battery, for it consists of seven separate galvanic cells. Previously, three-cell flat batteries were in use. But what can you do, the ignorance of the majority has formed its own slang, where everyone calls it batteries, even in the latest editions of the physics textbook a battery is written under the picture of a single galvanic cell, though it’s in brackets, but the students are not sophisticated in the peculiarities of the Russian written language; therefore BA-TA-REY-KA.
I am popularly speaking, in the modern sense, a battery is an element of the battery into which it is usually assembled.
“... Aziz! Battery!"
Mmm, learn the True Truth by heart? :)
Are the dimensions indicated in the article in elements A23 and A27 correct? Judging by the photo, the difference in length is quite significant, although in the text they are almost equal.
Dimensions are correct. The length is really almost the same for them, but the diameter of the A27 is 2.3 mm less. The picture may be misleading, but it is specially made to show that the batteries are of different sizes.
There were still 4.5 volts batteries during the Soviet era. Unfortunately no photos. They were called "square." They had folding contacts.