Batteries are actively used by people in everyday life. Many do not even think that such power sources, if used improperly, pose a danger to life and the environment. To avoid consequences, it is necessary to study the effect of elements on the body and the environment, as well as the recommendations of specialists on their disposal.
Content
Why are batteries dangerous?
Until now, most of the usual household appliances operate on autonomous power sources - on batteries. The label of such items usually indicates that they must not be disposed of through regular waste bins.
Such a warning is quite justified, because such power sources are dangerous - both people and nature are at risk. Not all people understand, not wanting to dispose of waste waste properly, they thereby contribute to environmental pollution.
For the environment
To meet the needs of customers, several types of batteries have been established for which a separate hazard class has been established.
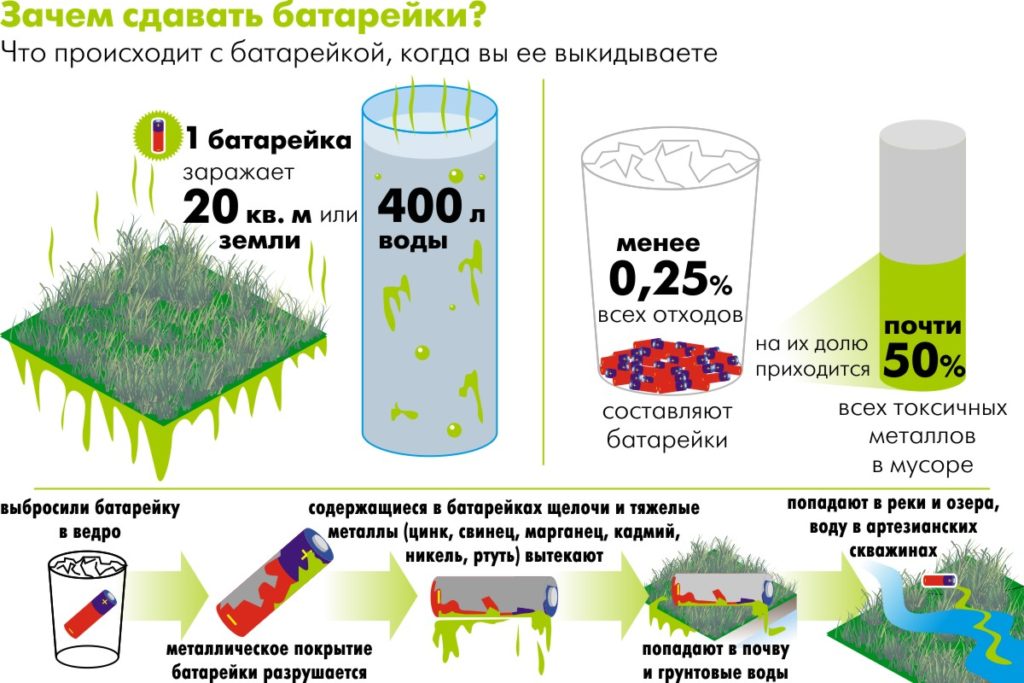
According to scientists, a single power source pollutes 20 square meters over time. m. of soil. Plants do not grow on poisoned earth, which further worsens the problem of enriching the planet with oxygen.
In order for the soil to be able to nourish the plants again, it will take a lot of effort to eliminate the consequences for several years. Further harmful substances seep into the groundwater, which increases the damage done.
Such significant harm is caused by the use of heavy metals in the production of batteries. The battery may contain particularly hazardous substances:
- lead;
- mercury;
- zinc;
- magnesium;
- tin;
- cadmium.
Ecology suffers from unregulated disposal of food sources - when they are burned. In the process of destruction, the old elements emit toxic substances that enter the atmosphere and subsequently fall to the earth in the form of precipitation, thereby polluting the entire affected area.
For human health
The harmfulness of batteries affects the human body. Damage is also caused by heavy metals. Depending on the type of power source, the consequences may be as follows:
- Lead. It affects the genitourinary and nervous system, bone tissue. With prolonged exposure, it "kills" red blood cells;
- Cadmium. Damages the pulmonary system and kidneys;
- Mercury. A particularly dangerous element that is rarely used in modern batteries. Despite the effectiveness, manufacturers were forced to abandon it, since batteries with such contents are unlikely to be applied to almost every organ. The respiratory, nervous and digestive systems are more affected;
- Zinc and nickel. May lead to impaired brain activity and destruction of the pancreas;
- Alkali. It can be called one of the most harmless elements, but with direct exposure it damages the skin and mucous tissues of the body.
The damage caused in each of the described cases increases significantly if the battery has oxidized or is leaking. For any violation of the integrity of the shell, it is important to immediately get rid of the power source in accordance with the established regulations, not allowing children and other family members to even touch it.
The effect of the battery on nature depending on the type
The composition of the batteries may vary - depending on the type.To determine the most non-hazardous options, it is worth considering the degree of influence of each species on the environment.
Saline
The cheapest option, where a solution of ammonium chloride acts as an electrolyte. In the composition of harmful substances are used to a minimum, therefore, the consequences for nature are also not so significant.
However, in any case, when decomposed in the soil, chemical reactions occur, which ultimately harms nature.
Alkaline
The most common battery. In the manufacture of electrodes, manganese dioxide and zinc are used. These two substances are considered hazardous, in particular this applies to zinc.
When hit in the ground, heavy metal infects living organisms, which makes the soil barren. Groundwater is simply poisoned by it.
Lithium
Lithium batteries consist of a lithium cathode and are characterized by relative safety for nature. But at the same time, during corrosion and depressurization, an explosion and fire can occur, as a result of which the environment will also suffer.
At the same time, it is unacceptable to dispose of them by throwing them in the bin, as chemically hazardous reactions may occur when interacting with other heavy metals.
Which are the most environmentally friendly and safe
When choosing batteries, it is better to give preference to rechargeable batteries, which can be charged when necessary with the help of special equipment, by connecting to a conventional outlet.
When buying, it is important to avoid purchasing batteries containing cadmium or mercury, which are hazardous substances. Information about the composition is reflected directly on the product, which avoids problems with the right choice.
Special attention should be paid to the expiration date and the external condition of the element. It’s better to overpay, but buying a battery is more expensive, thereby protecting yourself and family members.
What to do with a used battery
Finger batteries and other power sources must be disposed of with simple rules:
- throw away spent sources must be strictly in specialized containers;
- It is not permissible to dispose of items in ordinary rubbish bins with other household waste. A battery thrown in this way is harmful to the environment and living things;
- if it is not possible to discard the old source in specially designated containers, they should be stored in plastic containers in order to hand them over to special collection points;
- plastic containers should be placed in a safe place, ensuring the inability to access for children.
The most relevant slogans are “Hand over the battery - save nature” and “Save the environment together - do not dispose of used batteries” in the USA, Europe and Japan.
It is on the territory of these states that there are many places where it is possible to dispose of energy sources without unnecessary problems. Containers are located in most stores and institutions.
Unfortunately, in Russia there are almost no such points. People themselves are forced to look for reception points, which often either do not work, or are located at a considerable distance.
Have questions or have something to add? Then write to us about it in the comments, this will make the material more complete and accurate.